This is an old revision of the document!
Connection Tab (Login Dialog)
Connection tab allows you to configure general protocol-independent options for the connection.
Advertisement
You need to check Advanced options to reveal the tab.
More connection options are available on subtabs:
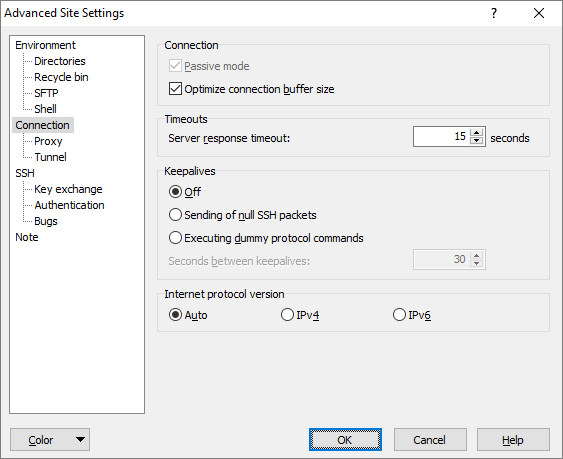
Passive Mode
Passive mode is special mode of FTP protocol. Use it, when you can connect to the server, but you are unable to setup a file transfer. To apply, when setting up a new session, tick the advanced optios button bottom left. Then in the list above select ftp.
Server Response Timeout
By the Server response timeout you define how long should WinSCP wait for an answer from the server before displaying window with option to Abort the connection. Note that the window does not block the waiting, so when it is displayed and the response is finally received it disappears itself.
Keepalives
Some servers (and also firewalls and routers on the way between the client and the server) disconnect clients if they do not receive any data from it within a defined period. In the Keepalives box, you may order WinSCP to send some dummy data in regular periods to avoid being disconnected. This period is defined with Seconds between keepalives.
Advertisement
WinSCP implements two methods for keepalives. For SFTP and SCP, the basic option is to send SSH-level keepalives implemented by null SSH packets (SSH ignore messages). Some servers may be configured not to count these packets as data and thus they will still disconnect clients sending them. Also if you use SSH-1 and your server suffers “SSH-1 ignore message” bug, this method will not work.
As an alternative WinSCP can send dummy commmands of the transfer protocol instead. For SFTP it is implemented as canonisation of path /. For SCP it is implemented as echo command.1 For FTP it is the only option and is implemented as randomly selected FTP protocol command with no effect.
Internet Protocol Version
This option allows the user to select between the old and new Internet protocols and addressing schemes (IPv4 and IPv6). The default setting is Auto, which means WinSCP will do something sensible and try to guess which protocol you wanted. (If you specify a literal Internet address, it will use whichever protocol that address implies. If you provide a hostname, it will see what kinds of address exist for that hostname; it will use IPv6 if there is an IPv6 address available, and fall back to IPv4 if not.)
If you need to force WinSCP to use a particular protocol, you can explicitly set this to IPv4 or IPv6.2
- With SCP this keepalive method does not work while WinSCP waits for user prompt in the middle of file transfer.Back
- The text is copy of PuTTY User Manual or was inspired by it.Back