This is an old revision of the document!
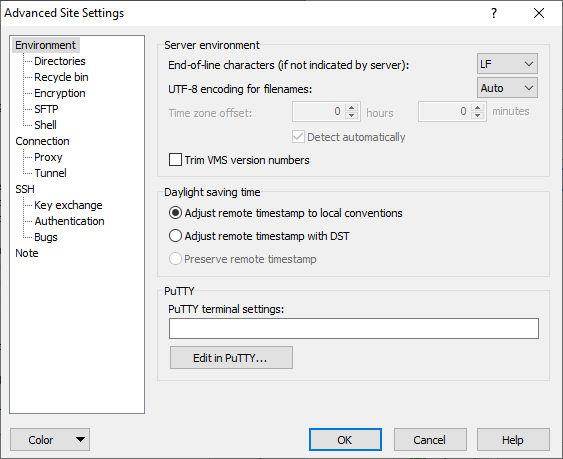
The Environment Page (Advanced Site Settings dialog)
The Environment page on the Advanced Site Settings dialog allows user to configure WinSCP adaptation for particular server/environment.
Advertisement
More environmental options are available on subpages:
- Directories (initial directories, directory cache)
- Recycle Bin
- Encryption (seamless file encryption)
- SFTP (SFTP protocol specific/compatibility options)
- SCP/Shell (shell and SCP protocol specific/compatibility options)
- FTP (FTP protocol specific options)
- S3 (S3 protocol specific options)
- WebDAV (WebDAV protocol specific options)
Refer to documentation of page sections:
Advertisement
Server Environment
End-of-line Characters
Use End-of-line characters to specify text file format used by the server. To allow text mode transfers, WinSCP needs to know the format of text files. Generally there is plenty of text file formats, almost every platform has it own format. WinSCP supports two most used formats, Unix and Windows. As most servers are run on Unix system, generally you may leave the default Unix format. If your server runs on Windows, select the Windows format. If you do not use text mode transfers, the option is not important for you.
With SFTP-4 and newer, the server tells itself what format it uses, so the configured option is not used.
With FTP, the option is disabled, as protocol specification defines the text file format. With WebDAV and S3, the option is disabled as the protocols do not support text mode transfers.
UTF-8 Encoding for Filenames
Usex UTF-8 encoding for filenames to configure if WinSCP should use UTF-8 (Unicode) encoding for filenames in communication with the server.
With default Auto value, WinSCP will try to autodetect if the server supports UTF-8. With SFTP protocol this means that UTF-8 is used for protocol version 4 and newer; for older versions, UTF-8 is used unless the server is known not to support UTF-81 or it sends strings not encoded with UTF-8. With FTP protocol this means that UTF-8 will be used when the server announces support for it. With SCP protocol this means that UTF-8 will be used when a LANG environment variable is set to “UTF-8” encoding.
Set the option to On to force usage of UTF-8 (useful for servers using UTF-8 natively). Set the option to Off to unconditionally disable usage of UTF-8 (for servers that does not use UTF-8).
With WebDAV and S3, the option is disabled as UTF-8 is always used with the protocols.
When not using UTF-8 encoding, WinSCP assumes the server is using the same legacy ANSI encoding as configured for local machine in Control Panel > Clock and Region > Region > Administrative > Language for non-Unicode programs.
Time zone Offset
The Time zone offset allows user to configure time zone difference of the server.
With SCP protocol the option is used to counterweight time difference between timestamp of remote file shown in directory listing and timestamp set on downloaded file, and vice versa. The difference is caused by fact that during transfer scp command usually uses UTC time format, while ls command may display time in local (for server) time format. The time difference can be negative. For example if the timestamps of remote files are two hours ahead of local files, set the option to -2 hours. Read about other issues with timestamps.
With FTP protocol the option is used to actually set the difference between local and remote time zone. Though it is used, when deprecated LIST command is used for directory listing, only. When using MLSD, the server must report all timestamps in UTC. To enable the option with FTP protocol, you need to opt to use LIST command explicitly by setting Use MLSD command for directory listing to Off. Though, you should use this only when the server does not support MLSD command or its implementation is buggy. The difference is automatically detected.2 If the detections fails, uncheck Detect automatically and set the difference manually.
Advertisement
The option is not available with SFTP, WebDAV and S3 protocols, as with them, the server must report all timestamps in UTC.
Trim VMS Version Numbers
Enable Trim VMS Version Numbers to remove VMS version numbers from filenames when transferring.
This ensures that on upload a new version of the file is created on the VMS system.
Daylight Saving Time
Some servers (mostly servers running on the older versions of Windows) incorrectly adjust file timestamp with start of DST. The Daylight saving time option allows you to counterweight the incorrect behavior.
The option is not supported with FTP protocol. The option is also not available with WebDAV and S3 protocols, as with them, no issues are known that would require it.
Select Adjust remote timestamp to local conventions, if the server behaves correctly and does not adjust file timestamp (typically Unix-based servers and Windows 7 and newer).
Select Adjust remote timestamp with DST, if the server does not behave correctly and adjusts file timestamp (Windows Vista/2008 and older).
Change the option, if timestamps of some files in the remote panel are shifted by one hour. This can happen either for already existing remote files, or for newly transferred files. For the latter case, please note that the option must be set correctly before transferring the files. It does not make sense to try to use it to adjust the incorrect timestamps of already transferred files.
Use the third option Preserve remote timestamp, if you want to see exact non-adjusted remote timestamp in remote panel. Drawback is that with the option selected, the synchronization functions will not work. This option is not available on Windows 7/2008 R2 and newer.
Read about other issues with timestamps.
PuTTY
In PuTTY terminal settings box, you can specify additional PuTTY settings that WinSCP should use, when opening session in PuTTY. Typically you will use it to set PuTTY terminal settings (like colors).
Click the Edit in PuTTY button to open PuTTY Configuration window. There, locate a stored session with a name like (Terminal settings for …). Click the Load button. Then edit PuTTY settings as you like (though do not modify the settings that can be controlled in WinSCP, like hostname, username, some SSH protocol settings, etc.). When done, click Save button and close PuTTY Configuration window. WinSCP will pick up the settings and load them to the PuTTY terminal settings box.
You can also specify the settings manually. Use PuTTY registry value names for the settings you want to set. For each settings use a format name=value. Separate multiple settings by a space. Textual values should be surrounded by double-quotes. For example, to double the size of PuTTY window and use gray for a default background color, use:
TermWidth=160 TermHeight=48 Colour2="105,105,105"
Advertisement
The box is not available, when there exists a PuTTY stored session with the same name as the WinSCP site. In that case, WinSCP uses the PuTTY stored session and no WinSCP settings.
Further Reading
Read more about Login dialog and Advanced Site Settings dialog.